Every year, millions of workers around the world suffer injuries or illnesses caused by unsafe working conditions. In the United States alone, in 2023, there were 5,283 fatal work-related injuries, according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. This equals a rate of 3.5 deaths for every 100,000 full-time workers.
While most organizations comply with basic safety regulations, compliance alone is not enough. What’s needed is a structured, proactive, and continuously improving approach to workplace safety and health. That’s where the Occupational Health and Safety Management System (OHSMS) standards come in.
Among these, the ANSI/ASSP Z10.0 standard provides a strong framework for organizations seeking to exceed compliance requirements. It helps businesses of all sizes establish a strong safety management system that protects workers, enhances performance, and aligns with long-term organizational objectives.
In this blog, we will look into what the ANSI Z10.0 standard is, why it matters, how it works, and how you can implement it effectively. Whether you’re managing a small business or leading safety operations in a large organization, this blog will help you understand how Z10.0 can be a practical tool for creating a safer and healthier workplace.
Understanding ANSI/ASSP Z10.0: The Foundation of Modern Safety Management
The ANSI/ASSP Z10.0 standard is a framework for managing occupational health and safety risks in the workplace. It was first introduced in 2005, revised in 2012, and most recently updated in 2019. The revisions have reflected advancements in safety science, systems thinking, and global harmonization of safety standards.
The Z10.0 standard was developed by ANSI (American National Standards Institute), a non-profit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards in the U.S., and the American Society of Safety Professionals (ASSP), a professional society focused on occupational safety and health.
These organizations collaborated to develop a practical, structured, and flexible safety management standard created to enhance workplace safety outcomes.
Scope and Purpose
The primary purpose of Z10.0 is to provide a structured approach for identifying, assessing, and managing workplace hazards to prevent injuries, illnesses, and fatalities. It promotes continuous improvement and is applicable across a wide range of industries and organization sizes.
It applies to Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems (OHSMS) and addresses the system-level processes needed to identify and control safety risks. It can be used by organizations of all sizes, including those with complex operations and smaller enterprises with limited resources.
Voluntary Nature of the Standard
Z10.0 is a voluntary standard, meaning it is not mandated by law or regulatory authorities. It is made to support organizations in improving their safety practices beyond regulatory compliance.
It does not require third-party certification, unlike ISO 45001. The focus is on performance improvement rather than formal recognition. Organizations can self-assess or use internal/external evaluations to measure conformance and progress.
This makes it a flexible tool for continuous improvement, allowing each organization to adopt it based on its specific needs, risks, and resources.
Compatibility with Other Standards
Z10.0 is created to align with other widely used management system standards, such as:
- ISO 45001 – Occupational health and safety management
- ISO 9001 – Quality management systems
- ISO 14001 – Environmental management systems
Essential areas of compatibility include the use of the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle for continuous improvement and emphasis on leadership commitment, worker participation, and risk-based thinking. It also includes encouraging integration with existing management systems to streamline processes, avoid duplication, and enhance overall efficiency.
This compatibility allows organizations to manage safety as part of a broader business management strategy, rather than in isolation.
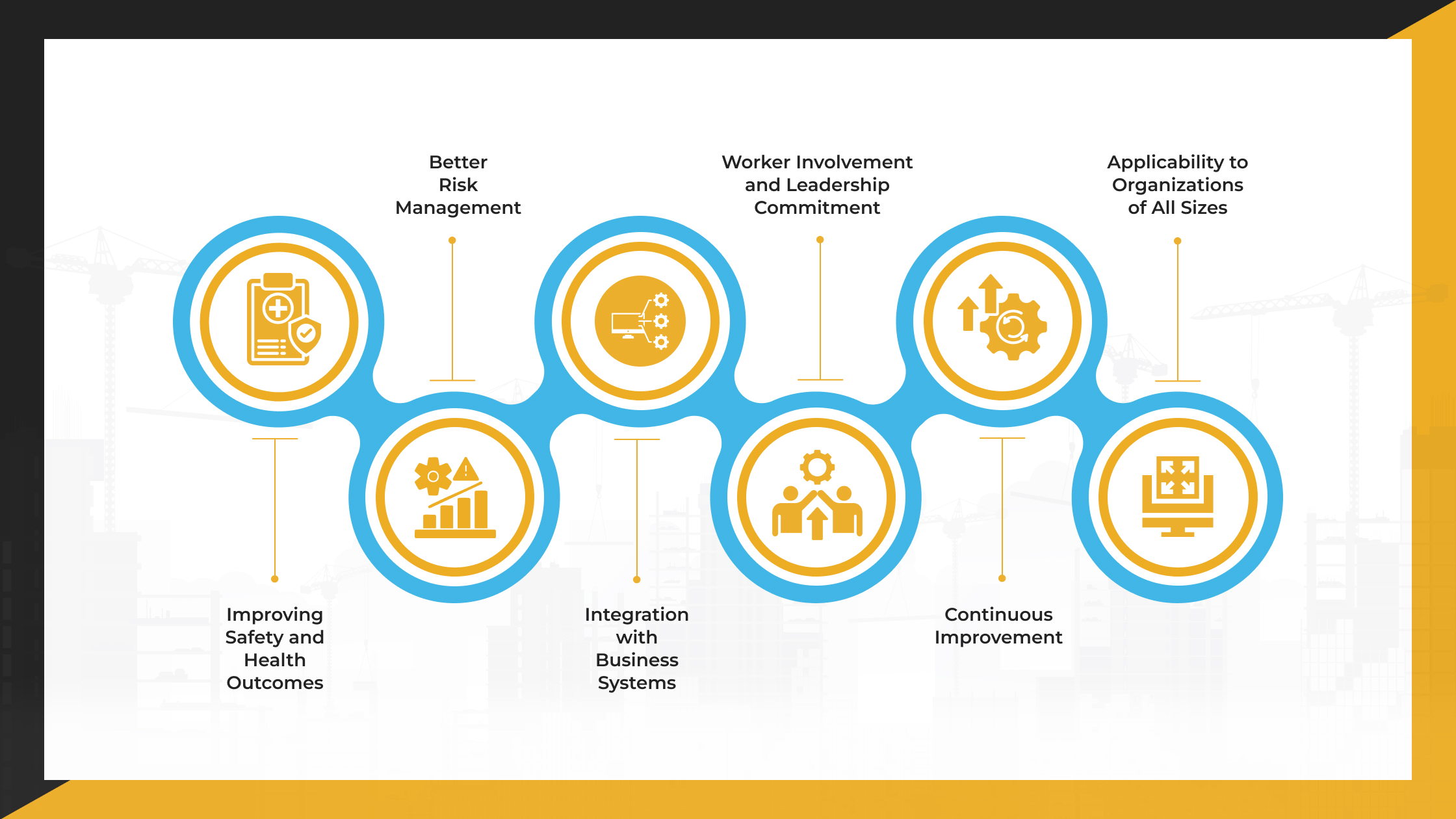
The Strategic Benefits of Implementing ANSI Z10.0
Before implementing ANSI Z10.0, it’s essential to understand why it matters. Below are the key benefits and the rationale for adopting this standard in your organization
-
Improving Safety and Health Outcomes
Z10.0 provides a structured approach to reduce workplace injuries, illnesses, and fatalities. By focusing on identifying hazards and managing risks before incidents occur, the standard helps create safer work environments. This reduces both human and financial costs associated with workplace incidents.
-
Better Risk Management
The standard emphasizes systematic processes for identifying, assessing, and controlling occupational health and safety hazards. It encourages organizations to move from reactive to preventive risk management.
Through formal hazard identification and risk analysis, companies can better understand potential threats and implement appropriate controls before they cause harm.
-
Integration with Business Systems
Z10.0 is designed to align with other management system standards, such as ISO 9001 (quality management) and ISO 14001 (Environmental Management). This compatibility allows organizations to integrate safety into their overall business strategy.
It supports system-level thinking by connecting safety performance with broader operational goals, enabling efficiency and consistency across departments.
-
Worker Involvement and Leadership Commitment
The standard promotes active participation of workers at all levels and requires strong commitment from leadership. Involving employees in decision-making and hazard identification enhances the relevance and effectiveness of safety practices.
Leadership commitment ensures that adequate resources are allocated and that safety becomes part of the organizational culture.
-
Continuous Improvement
Z10.0 follows the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle to support ongoing improvement of safety systems. It requires regular monitoring, internal audits, incident investigations, and management reviews.
These feedback mechanisms help organizations learn from both failures and successes, allowing them to adapt and refine their safety programs over time.
-
Applicability to Organizations of All Sizes
The standard is scalable and can be implemented by organizations of any size or industry. It includes specific guidance and tools for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that may have limited resources.
This flexibility ensures that even smaller organizations can develop effective occupational health and safety management systems tailored to their needs.
What’s New in ANSI Z10.0-2019: Essential Updates You Should Know
The 2019 revision of ANSI Z10.0 introduced several important updates to reflect modern safety practices and systems thinking. Below are the essential changes and their implications for organizations implementing the standard.
-
System Thinking
The 2019 revision introduces a stronger focus on systems thinking, encouraging organizations to understand how various processes interact with each other. Instead of viewing safety controls as isolated tasks, the standard promotes a dynamic approach where changes in one area can impact others.
This helps identify root causes of safety issues more effectively and manage them across the entire system.
-
Enhanced Worker Input and Emphasis on Health
Z10.0-2019 expands the role of workers in determining acceptable levels of risk. Employees are encouraged to participate not only in identifying hazards but also in setting the thresholds for what is considered safe.
In addition, the updated version places greater emphasis on occupational health, including psychosocial risks, ergonomic factors, and chronic exposure hazards, thereby moving beyond immediate physical safety considerations.
-
Distinction Between Hazards and OHSMS Issues
The revised standard makes a clear distinction between hazards and broader Occupational Health and Safety Management System (OHSMS) issues.
While hazards refer to direct sources of harm (e.g., machinery, chemicals), OHSMS issues encompass system-level factors, including deficiencies in procedures, a lack of leadership support, gaps in legal compliance, or external expectations. Recognizing this separation helps organizations take a more strategic approach to safety management.
-
Emphasis on Organizational Learning
Z10.0-2019 places significant importance on organizational learning. It encourages companies to not only learn from incidents and near-misses but also from what went well.
This helps create a culture that values continuous feedback and improvement. Learning is treated as a long-term asset that contributes to the sustainability of the safety program.
-
Alignment with ISO 45001
The updated Z10.0 standard is better aligned with ISO 45001, the international standard for occupational health and safety management systems. While Z10.0 remains a unique framework, this alignment helps organizations that wish to integrate both standards.
The goal is to reduce duplication, allow smoother system integration, and support organizations operating in global environments.
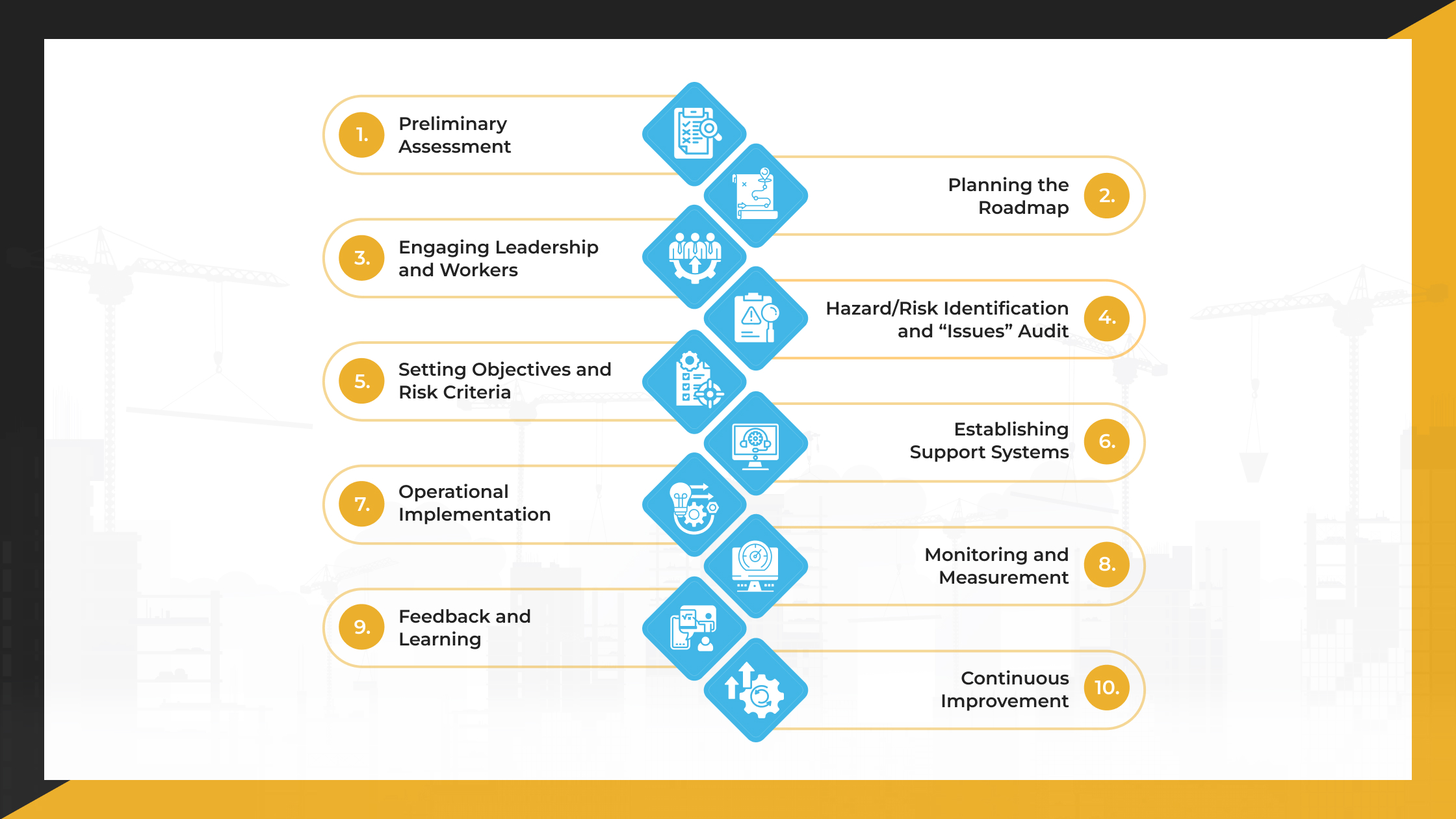
Best Practices for ANSI Z10.0 Implementation in Your Organization
Implementing ANSI Z10.0 requires a structured approach to ensure its principles are applied effectively. Below is a list of some of the essential best practices to help organizations adopt the standard successfully.
-
Preliminary Assessment
Start by evaluating the current status of your Occupational Safety and Health (OSH) program. Identify existing strengths, weaknesses, and any gaps compared to the Z10.0 requirements.
Leadership involvement is essential at this stage to ensure a commitment to providing the necessary resources and support for implementation.
-
Planning the Roadmap
Develop a clear implementation plan. Define the project’s scope, whether it includes the entire organization or specific departments. Allocate resources such as time, budget, and personnel. Set achievable timelines and assign accountability for each step to ensure progress.
-
Engaging Leadership and Workers
Involve top management and workers from the beginning. Define roles and responsibilities clearly. Leadership must visibly support the initiative, while worker participation ensures practical insights and fosters ownership of the safety program across all levels.
-
Hazard/Risk Identification and “Issues” Audit
Conduct a thorough assessment of workplace hazards and risks. In addition to physical hazards, identify broader “OHSMS issues” such as regulatory gaps, process deficiencies, or stakeholder concerns. This forms the basis for developing targeted controls and improvements.
-
Setting Objectives and Risk Criteria
Set specific, measurable OSH objectives aligned with your organization’s goals. Involving both management and employees in defining acceptable levels of risk is essential. This helps guide decision-making and sets a clear direction for performance improvement.
-
Establishing Support Systems
Build the necessary support systems to implement and maintain the program. This includes providing training for employees, ensuring effective communication at all levels, and managing documentation such as procedures, manuals, and records. These elements ensure consistency and accountability.
-
Operational Implementation
Put the planned controls into action. This includes applying hazard controls, managing change processes, preparing for emergencies, and ensuring the safety of contractors and personnel. All operational activities should adhere to the system’s guidelines and be regularly monitored for compliance.
-
Monitoring and Measurement
Track safety performance using both leading indicators (such as training completion and inspections) and lagging indicators (such as injury rates or incidents). Conduct regular internal audits, inspect processes, and investigate any deviations or incidents to identify root causes.
-
Feedback and Learning
Use findings from incidents, near misses, audits, and successes to improve the system. Feedback mechanisms should be structured and lead to actionable changes.
Learning should be shared across the organization to avoid repeated issues and replicate successful practices. Conduct periodic management reviews to assess whether the OSH system is functioning as intended.
-
Continuous Improvement
Make continuous improvement a core part of the system. Based on performance data and lessons learned, refine processes, update objectives, and adjust controls.
Where applicable, integrate the Z10.0 system with other management systems, such as quality (ISO 9001) or environmental (ISO 14001), to streamline operations and reduce duplication.
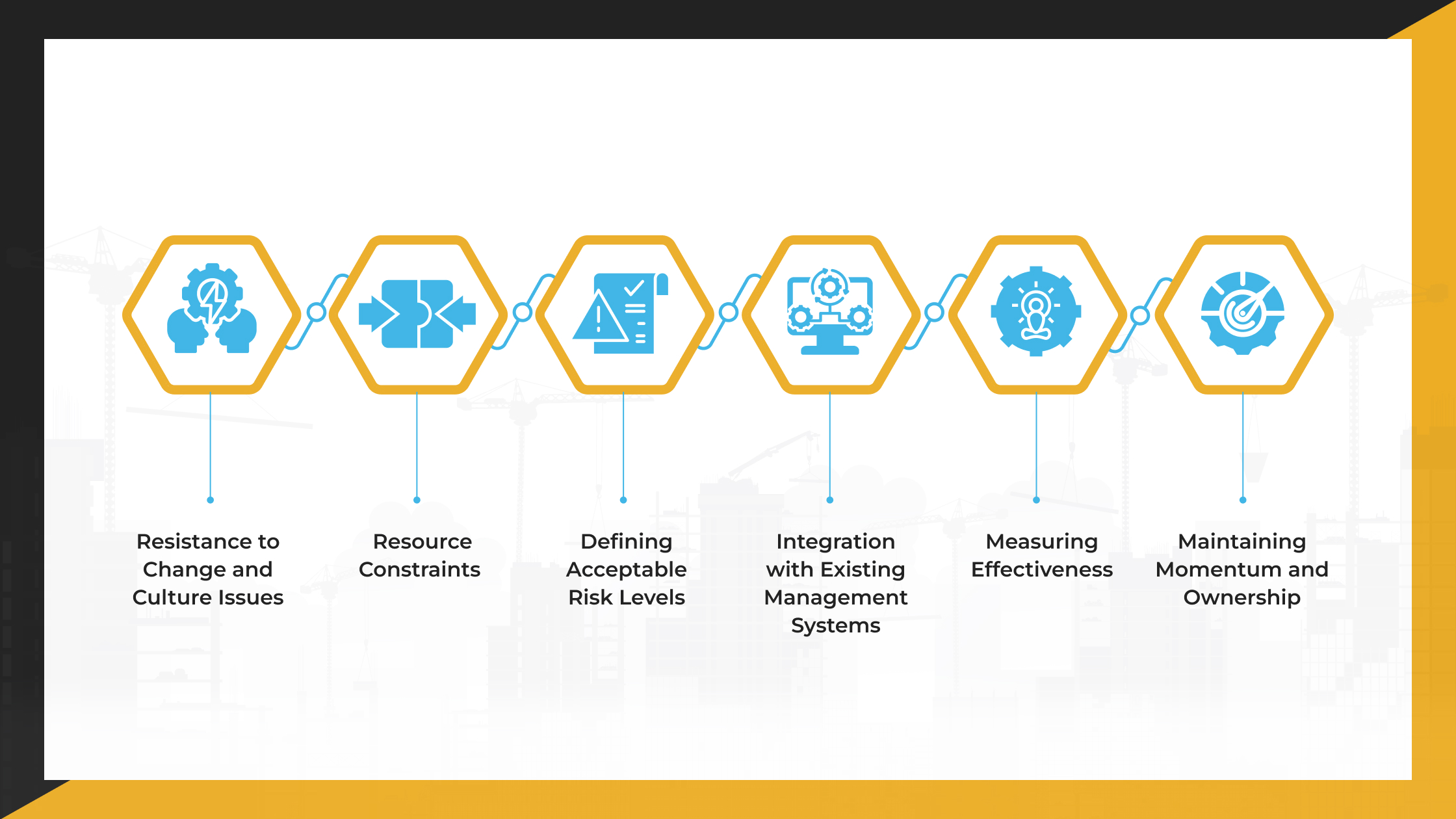
Challenges in Implementing ANSI Z10.0 and How to Overcome Them
While ANSI Z10.0 provides a strong framework for enhancing workplace safety, organizations may encounter practical challenges during the implementation process. Below are the common obstacles and proven strategies to address them effectively.
-
Resistance to Change and Culture Issues
Many organizations face resistance when introducing new systems. Employees and even some managers may be accustomed to existing routines and view Z10.0 implementation as unnecessary or disruptive. This cultural resistance can hinder or impede progress.
Build awareness about the benefits of Z10.0 through consistent communication. Involve employees early in the process and encourage them to provide feedback. Leadership must visibly support the change to set the tone and build trust.
-
Resource Constraints
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) often face challenges due to limited resources. Allocating time, trained staff, and financial resources for implementing a comprehensive safety management system can be challenging.
Adopt a phased implementation strategy to spread resource demands over time. Focus on high-risk areas first and build from there. Utilize simplified guidance manuals, such as GM-Z10.100-2019 and GM-Z10.101, to help SMEs reduce complexity and cost.
-
Defining Acceptable Risk Levels
Understanding and setting acceptable levels of risk is a technical and collaborative task. Misjudging risk can lead to under- or over-control, affecting both safety and productivity.
Engage both safety professionals and workers in determining acceptable risk thresholds. Use risk assessment tools and align risk tolerance with the organization’s values and operational needs. Regularly review risk levels based on performance data and operational changes.
-
Integration with Existing Management Systems
Organizations that already follow standards like ISO 9001 or ISO 14001 may find it challenging to integrate Z10.0 without creating duplicate processes or operational silos.
Map the Z10.0 elements to existing systems using a cross-reference approach. Identify overlapping areas and unify procedures where possible. Align documentation and reporting structures to streamline operations and enhance efficiency.
-
Measuring Effectiveness
Tracking the success of a safety management system requires the use of meaningful and consistent metrics. Many organizations struggle to select the right indicators or interpret them effectively.
Use a combination of leading indicators (such as training frequency and near-miss reports) and lagging indicators (such as incident rates). Ensure metrics are aligned with organizational goals and regularly reviewed. Adjust indicators as needed based on insights from audits and reviews.
-
Maintaining Momentum and Ownership
Initial enthusiasm can fade if the system doesn’t produce visible results quickly. Without sustained involvement, the safety program may lose relevance over time.
Set short-term, achievable goals to build early success. Share progress and improvements regularly with all levels of the organization. Create ownership by assigning clear roles and recognizing contributions. Management reviews should include plans to re-energize efforts as needed.
ANSI Z10.0 vs ISO 45001: What Sets Them Apart
Although ANSI Z10.0 and ISO 45001 share similar principles for occupational health and safety management, they differ in scope, focus, and application. Below is a clear comparison of their key differences to help organizations choose the right approach.
| Feature / Element | ANSI/ASSP Z10.0 | ISO 45001 |
| Primary Focus | Performance improvement and system maturity | Certification and global compliance |
| Certification Requirement | Not created for certification | Created for formal third-party certification |
| System Thinking Emphasis | Strong emphasis on the interdependence of systems | Less explicit focus on systems interconnectivity |
| Prescriptiveness | More detailed guidance in some areas | More flexible, general framework |
| Health vs Safety | Broader focus on health (e.g., ergonomics, psychosocial) | Primarily focused on safety and compliance |
| Worker Involvement in Risk Setting | Direct involvement in setting acceptable risk levels | Encourages participation but is less specific |
| Guidance and Tools | Includes advisory manuals (e.g., GM-Z10.100, GM-Z10.101) | Limited official implementation guidance |
| Integration with Other Standards | Compatible but more focused on internal system design | Structured for easy integration (Annex SL format) |
When Your Organization Should Choose ANSI Z10.0 (or Combine It with ISO 45001)
- Use Z10.0 if your organization is focused on improving internal safety systems without seeking certification. It’s beneficial for U.S.-based companies looking to align with OSHA expectations or SMEs that need detailed guidance.
- Use ISO 45001 if international certification, supply chain compliance, or global operations are priorities.
- Use Both if you want to build a strong, performance-driven system (Z10.0) while also meeting international certification standards (ISO 45001). Z10.0 can serve as an internal improvement tool that complements ISO’s external certification framework.
Enhance Your Safety Standards with Safe T Professionals
At Safe T Professionals, we are dedicated to elevating safety standards through our expert consulting and staffing services. By proactively addressing and preventing safety issues and equipping your workforce with the necessary knowledge and tools, we help create a safer work environment.
Partner with Safe T Professionals to enhance your company’s safety protocols and ensure compliance with industry standards. Whether you are looking to fill safety-specific roles or need expert consultation to mitigate workplace hazards, we are here to help.
Connect with us today!